Did you think you had to avoid watermelon with diabetes? You'll be surprised to find out watermelon is on the low glycemic foods list and a good source of vitamins and minerals!
Watermelon had a high glycemic index until it was updated in the latest international glycemic tables, making it a low glycemic fruit.
It's a great fruit for diabetics, but portioning is still important to blood sugar management.

Jump to:
Watermelon Glycemic Index
Watermelon use to be a high glycemic fruit according to the 2008 glycemic index evaluation. On a scale of 1 to 100, with the high glycemic range starting at 70, it landed at 80.
The updated review of 2021 states watermelon is low glycemic with a value of 50.
However, glycemic index is assigned without consideration of serving size. Glycemic load (GL) factors in portion sizes to paint a better picture of how foods actually affect blood glucose.
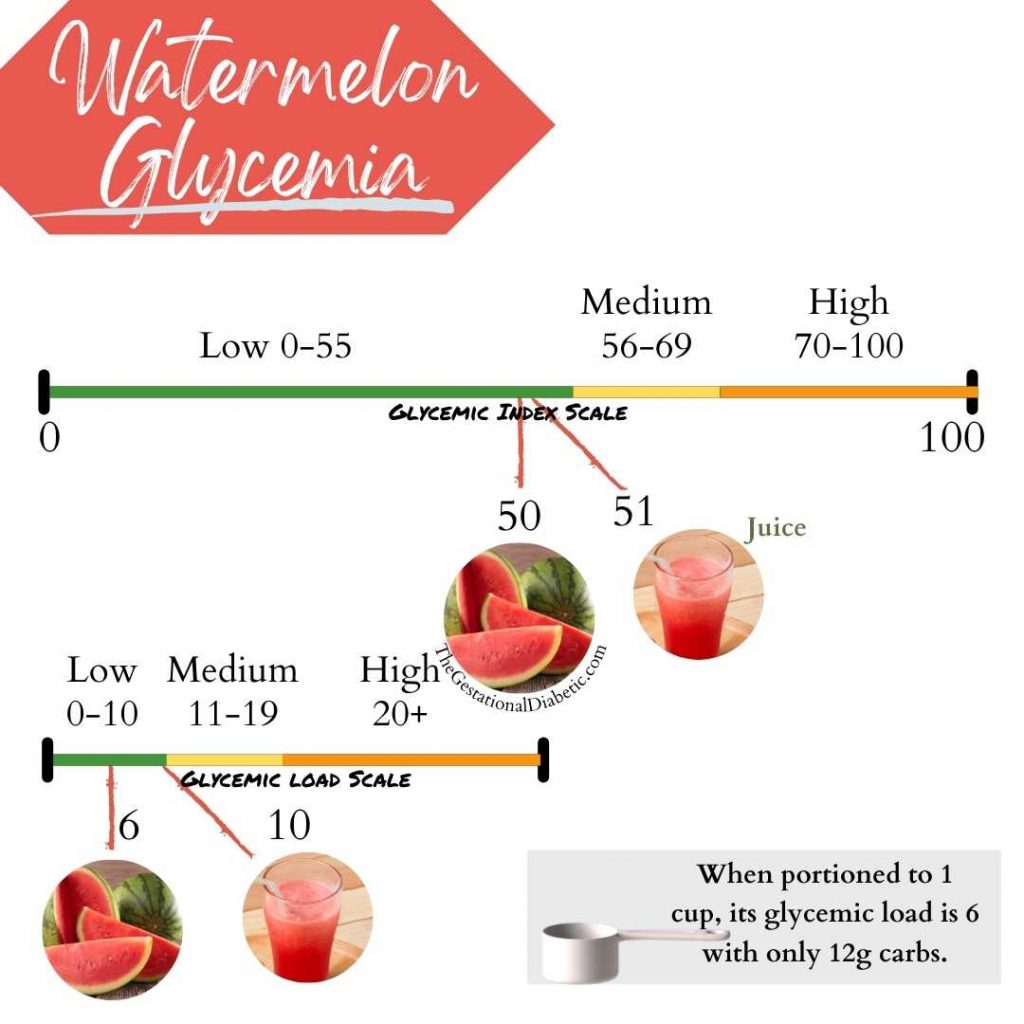
Even though its glycemic value dropped 30 points, its glycemic load dropped only 3 points from 9 to 6; both which fall in the low glycemic load range.
Is Watermelon Healthy for Diabetics?
Yes! Watermelon is a low GI fruit and has a low glycemic load as well, meaning when it's reasonably portioned watermelon has a small effect on blood sugar.
When eaten in large quantities, watermelon can cause a blood sugar spike, just like most other food with carbs.
This image shows pairing suggestions that add protein or healthy fats to help balance macronutrients.

Watermelon Nutrition (1 cup serving, fresh)
Fresh watermelon, is considered a "whole fruit" and is a healthy food for diabetics. The below nutrition data is for fresh watermelon; not juiced, dried, or otherwise processed.
- Calories - 46
- Fat - 0g
- Carbs - 12g
- Fiber - 1g
- Sugar - 9g
- Protein - 1g
- Vitamin C - 37%
- Iron - 3%
- Vitamin B6 - 5%
- Magnesium - 7%
Per the USDA, it's an excellent source of Vitamin C, and a good source of Vitamin A and beta carotene.
Vitamin C and beta-carotene are key antioxidants that neutralize free radicals. These nutrients, along with watermelon's lycopene, help lower the risk of cancer and promote heart health by lowering cholesterol and blood pressure.
Eating Watermelon Benefits for Diabetes
What makes watermelon a great fruit for diabetes is that it has magnesium and plenty of water, both of which help regulate blood sugar.
- Magnesium is a key player in glucose control. Increased intake of magnesium is known to decrease blood glucose levels.
See the best magnesium food sources for more ways to incorporate it into your diet. - Possible weight loss - A healthy weight is good for insulin resistance. Because of its high water content, watermelon has low calories, a negligible amount of fat, and few carbs; all of which aid weight loss.
Water in Watermelon
Water's role in blood glucose management is to flush glucose out of the blood.
Watermelon is 91% water! This is watermelon's biggest glucose regulator.
With 91% water, watermelon will hydrate you and simultaneously flush sugars out of the blood.

How Much Watermelon Should a Diabetic Eat?
No two cases of diabetes are the same, so there's no hard and fast answer to this question.
When you eat it, and what you eat it with, also factor into the question.
It's best to avoid eating carbs on their own (without protein or fat), so a serving of fruit as an after-meal dessert is a great way to balance your carb intake and avoid added sugars.
Watermelon can star in this role! Though most of its carbs are sugars, it does not fit the definition to be claimed "high in" sugar. Compared to what you'd consume in a dessert, it's low sugar!
Start with a small portion, and be sure to drink your Ovaltine 🙂 - I mean, be sure to factor the carbs into your allowance.
Watermelon Juice
Carbohydrates in liquid form, like fruit juices and smoothies, are digested more quickly than carbs in solid form, like apples, oranges, and other whole fruits. The 2021 glycemic review shows watermelon juice has a glycemic index of 51 and a glycemic load of 10.
Note:
Store-bought fruit juice is often made from concentrate, making the carb count higher than if you were to eat the fruit itself.
FAQ
Yes, all carbohydrate-containing foods raise blood sugar, but watermelon also has a high water content and magnesium, both of which help regulate blood glucose.
No; by definition, "high in" means 20% or more of the daily value: Watermelon does not meet that threshold. In a serving size of 1 cup, 9 of the 11 carbs are natural (not added) sugars.
No. The sugars in watermelon are naturally occurring sugars, not added sugars. They are also simple sugars. These are okay in moderation; plus, watermelon's benefits far outweigh the concern of its sugar content.
Yes! Watermelon is hydrating, nutrient-rich, and naturally colored and sweetened. Gatorade does not nutritionally compare to watermelon. Though Gatorade has expanded its offerings, their main products contain only sodium and potassium as nutrients, harmful dyes, and added sugars. It was made to be a hydrating electrolyte-replenisher for those who sweat heavily, like athletes.
Summary
Watermelon has a low glycemic index of 50. It's full of electrolytes, and its magnesium and high water content help to regulate blood sugar levels.
More Glycemic Index Info
- Can a diabetic eat mango?
- Fruits for diabetics
- Sweet potato diabetes info
- Potatoes glycemic index
- Carrot glycemic index








Linc
Measuring food by the cup, or 'slice', or 1/2 box is a terribly inaccurate method of measurement. Measuring by the gram, milliliter, or ounce, is far more accurate.
How many grams of sliced apples fit into a 1 cup container? It depends on the size of the slices, doesn't it? It depends on the air spaces between slices. You might fill the cup with slices (1 cup), but if you weigh it, it only weighs 113 grams. Now, weigh one cup of applesauce. It weighs 265 grams. BIG difference.
Stop measuring food by using volume measurements. Measure food by its weight instead. Get a scale, not a measuring cup.
When we are trying to be accurate with respect to glycemic index, try to be more accurate with unit size measurements.